基本概念
OLTP
OLTP(On-Line transaction processing)翻译为联机事物处理;主要对数据库增删改查。
OLTP 主要用来记录某类业务事件的发生;数据会以增删改查的方式在数据库中更新处理操作,要求实施性强,稳定性高,确保数据及时更新。
OLAP
OLTP(On-Line Analytical Procesing)翻译为联机分析处理;主要对数据库查询。
当数据积累到一定程度,我们需要对过去发生的事情做一个总结,就需要将过去一段时间产生的数据拿出来统计分析,获取我们需要的信息。
SQL
结构化查询语言(Structured Query Language)简称 SQL,是一种特殊目的的编程语言,用来存取数据和查询、更新和管理关系数据库系统。SQL 是关系数据库系统的标准语言。
关系型数据库包括:MySQL, SQL Server, Oracle, Sybase, postgreSQL 和 MS Access 等;
SQL 包括:DQL,DML,DDL,DCL 和 TCL。
DQL
Data Query Languate:数据查询语言;
- select :从一个或多个表中检索特定的记录。
DML
Data Manipulate Language:数据操作语言;
- insert:插入记录;
- update:更新记录;
- delete:删除记录。
DDL
Data Define Language:数据定义语言;
- create:创建一个新的表、表的视图、或在数据库中的对象;
- alter:修改现有的数据库对象,例如修改表的属性或者字段。
MySQL 体系结构
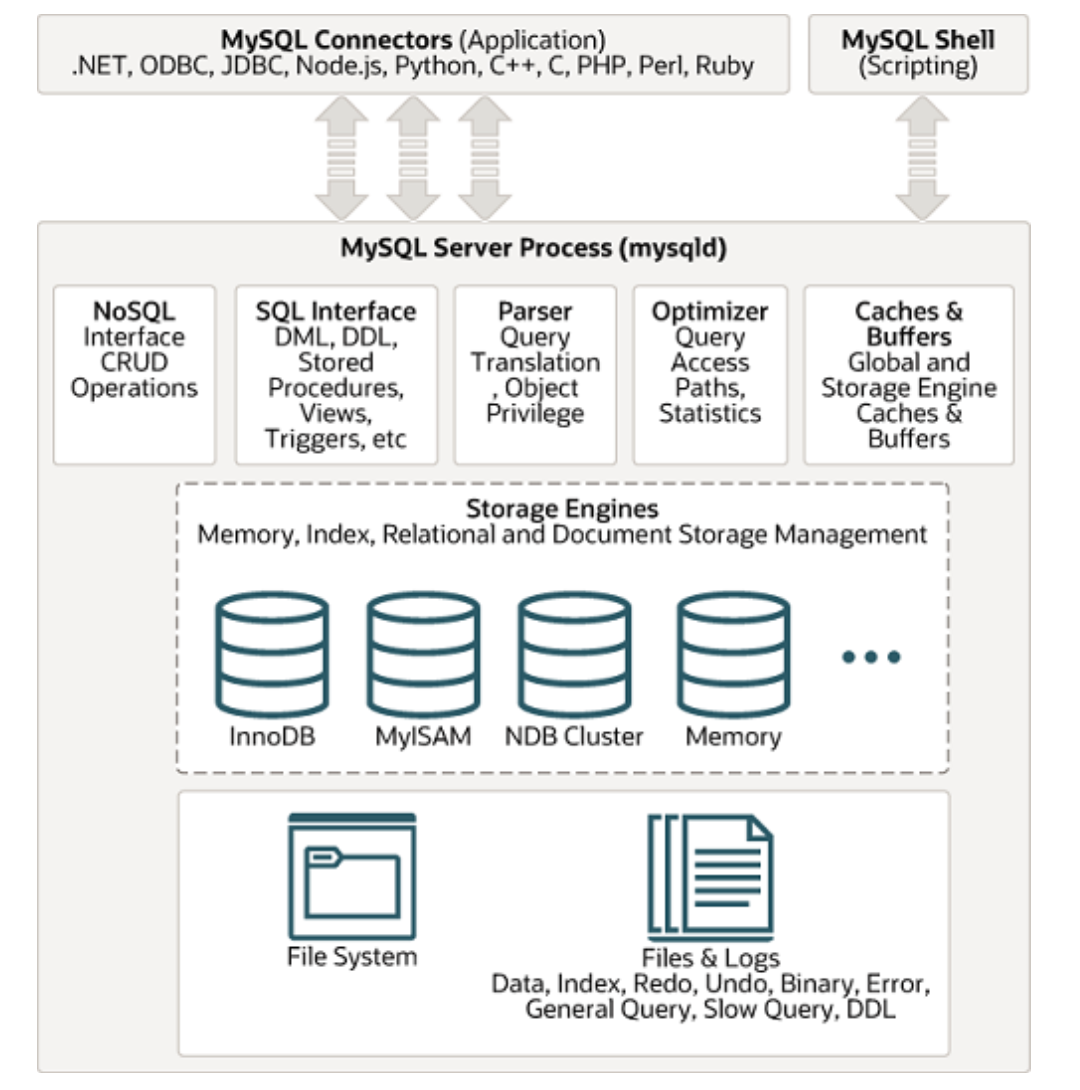
image.png
从图中可以看到 MySQL 的组成部分:
- 连接池组件
- 管理服务和工具组件
- SQL 接口组件
- 查询分析器组件
- 缓冲组件
- 插件式存储引擎
- 物理文件
连接者
不同语言的代码程序和数据库交互(SQL 交互)。
MySQL 内部连接池
管理缓冲用户连接、用户名、密码、权限校验、线程处理等需要缓存的需求。
查询解析器
将 SQL 对象交给解析器验证和解析,并生成语法树。
查询优化器
SQL 语言执行前使用查询优化器进行优化。
缓冲组件
数据库设计范式
为了建立冗余较小,结构合理的数据库,设计数据库时必须遵循一定的规则。在关系型数据库中这种规则称为范式。范式是符合一种设计要求的总结。想要设计一个结构合理的关系型数据库,必须满足一定的范式。
范式一
确保每一列保持原子性,数据库表中所有字段都是不可分解的原子值;
例如某个表中有一个地址字段,如果需要经常访问地址字段中的城市属性,则需要将该字段拆为多个字段,省份、城市、详细地址等。
范式二
确保表中每列都和主键相关,而不能只与主键的某一部分相关;
范式三
确保每一列都和主键直接相关,而不是间接相关;减少冗余;
反范式
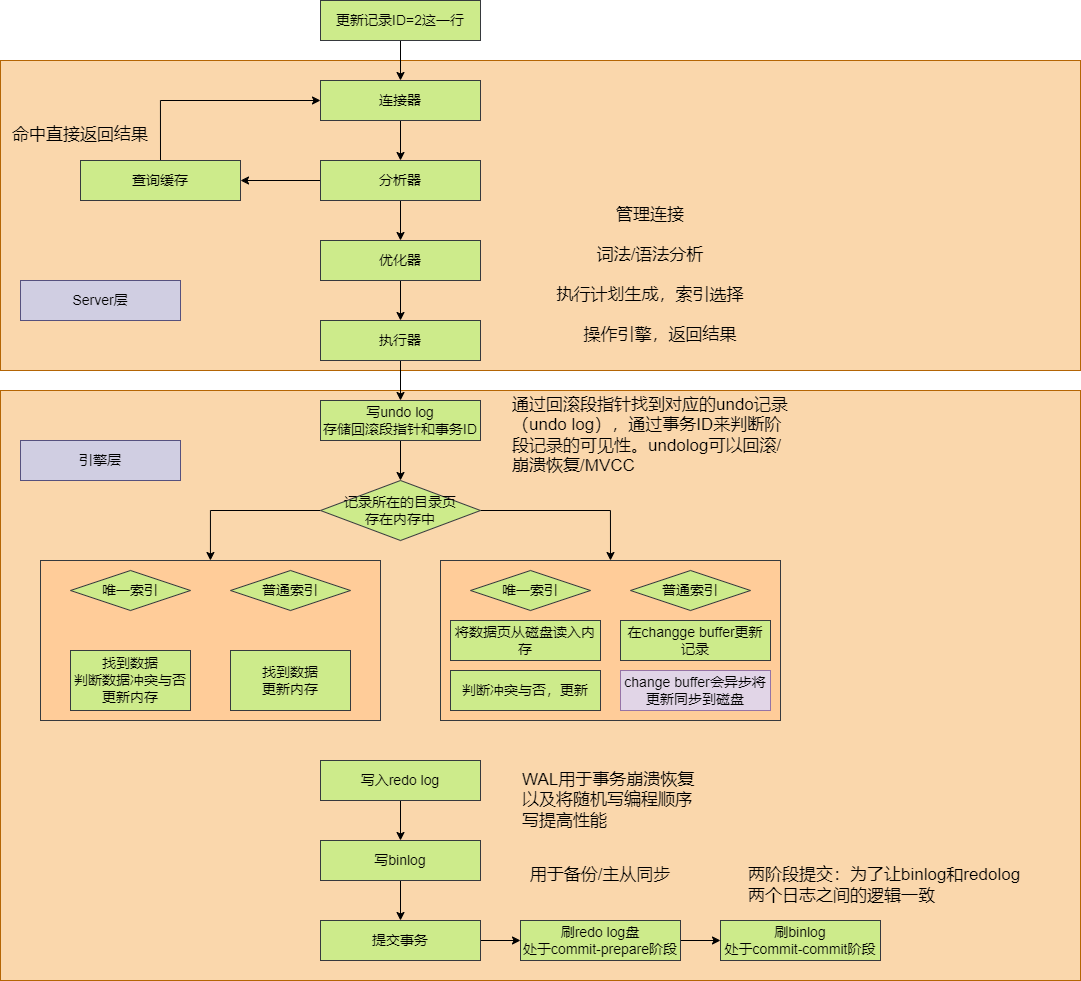
CRUD
执行过程
创建数据库
- 01
create database `firstdb` default character set utf8;
删除数据库
- 01
drop database `firstdb`;
选择数据库
- 01
use `firstdb`;
创建表
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
create table if not exists `animaltb` (
`id` int unsigned auto_increment comment '编号',
`type` varchar(10) not null comment '类别',
`height` decimal(8, 2) not null comment '身高',
primary key (`id`)
)engine = innoDB default charset = utf8 comment = '动物表';
删除表
- 01
drop table `animaltb`;
清空数据表
- 01
- 02
truncate table `animaltb`; -- 截断表 以页为单位(至少有两行数据),有自增索引的话,从初始值开始累加
delete table `animaltb`; -- 逐行删除,有自增索引的从之前的继续累加
增
- 01
insert into `animaltb` (`type`, `height`) values ('lion', 7.9);
删
- 01
delete from `animaltb` where id = 3;
改
- 01
- 02
update `animaltb` set `type` = 'lion' where id = 2;
update `animaltb` set `height` = `height` + 1 where id = 3;
查
- 01
select field1, field2, ...fieldn from table_name [where clause];
高级查询
准备
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
create database greatselect;
use greatselect;
drop table if exists `class`;
create table `class` (
`cid` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`caption` varchar(32) not null,
primary key (`cid`)
)engine = innoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=5 default charset = utf8;
create table if not exists `teacher` (
`tid` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`tname` varchar(32) not null ,
primary key (`tid`)
) engine = innoDB auto_increment=6 default charset = utf8;
drop table if exists `course`;
create table `course` (
`cid` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`cname` varchar(32) not null,
`teacher_id` int(11) not null,
primary key (`cid`),
key `fk_course_teacher` (`teacher_id`),
constraint `fk_course_teacher` foreign key (`teacher_id`) references `teacher` (`tid`)
)engine = innoDB auto_increment=5 default charset = utf8;
drop table if exists `student`;
create table `student` (
`sid` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`gender` char(1) not null ,
`class_id` int(11) not null ,
`sname` varchar(32) not null ,
primary key (`sid`),
key `fk_class` (`class_id`),
constraint `fk_class` foreign key (`class_id`) references `class` (`cid`)
)engine = innoDB auto_increment=17 default charset = utf8;
drop table if exists `scocre`;
create table `score` (
`sid` int(11) not null auto_increment,
`student_id` int(11) not null ,
`course_id` int(11) not null ,
`num` int (11) not null ,
primary key (`sid`),
key `fk_score_student` (`student_id`),
key `fk_course_id` (`course_id`),
constraint `fk_score_student` foreign key (`student_id`) references `student` (`sid`),
constraint `fk_score_course` foreign key (`course_id`) references `course` (`cid`)
)engine = innoDB auto_increment=53 default charset = utf8;
show tables;
基础查询
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
-- 全部查询
select * from student;
-- 只查询部分字段
select `sname`, `class_id` from student;
-- 别名 列名 不要用关键字
select `sname` as ‘姓名’, `class_id` as '班级ID' from student;
-- 把查询出来的结果的重复记录去掉
select distinct `class_id` from student;
条件查询
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
-- 查询姓名为lennlouis的学生信息
select * from `student` where `name` = 'lennlouis';
-- 查询性别为 男,且班级为 2 的学生信息
select * from `student` where `gender` = '男' and `class_id` = 2;
范围查询
- 01
- 02
-- 查询班级id 1 到 3 的学生信息
select * from `student` where `class_id` between 1 and 3;
判空查询
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
-- is null 判断造成索引失效
select * from `student` where `class_id` is not null;
select * from `student` where `class_id` is null;
-- 字符串不为空
select * from `student` where `gender` <> '';
-- 字符串为空
select * from `student` where `gender` = '';
模糊查询
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
-- 使用 like关键字,“%”代表任意数量的字符,“_”代表占位符
-- 查询名字为 m开头的学生信息
select * from `teacher` where `tname` like 'l%';
-- 查询姓名里第二个字为 ‘e’的小学生的信息
select * from `teacher` where `tname` like '_e%';
分页查询
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
-- 分页查询主要用于查看第 N条 到第 M条的信息,通常和排序查询一起使用
-- 使用limit关键字,第一个参数表示从条记录开始显示,第二个参数表示要显示的数目。表中默认第一条记录的参数为0
-- 查询第二条到第三条内容
select * from `student` limit 1, 2;
查询后排序
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
-- 关键字:order by field, asc:升序, desc:降序
select * from `score` order by `num` asc;
\-- 多个字段排序
select * from `score` order by `course_id` desc, `num` desc
聚合查询
| 聚合函数 | 描述 |
| ——– | ——— |
| sum () | 计算某一列的总和 |
| avg () | 计算某一列的平均值 |
| max () | 某一列的最大值 |
| min () | 某一列的最小值 |
| count () | 某一列的行数 |
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
select sum(`num`) from `score`;
select avg(`num`) from `score`;
select max(`num`) from `score`;
select min(`num`) from `score`;
select count(`num`) from `score`;
分组查询
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
-- 分组加 group_concat
select `gender`, group_concat(`age`) as ages from `student` group by `gender`;
-- 可以把查询出来的结果根据某个条件来分组显示
select `gender` from `student` group by `gender`;
-- 分组加聚合
select `gender`, count(*) as num from `student` group by `gender`;
-- 分组条件
select `gender`, count(*) as num from `student` group by `gender` having num > 6;
联表查询
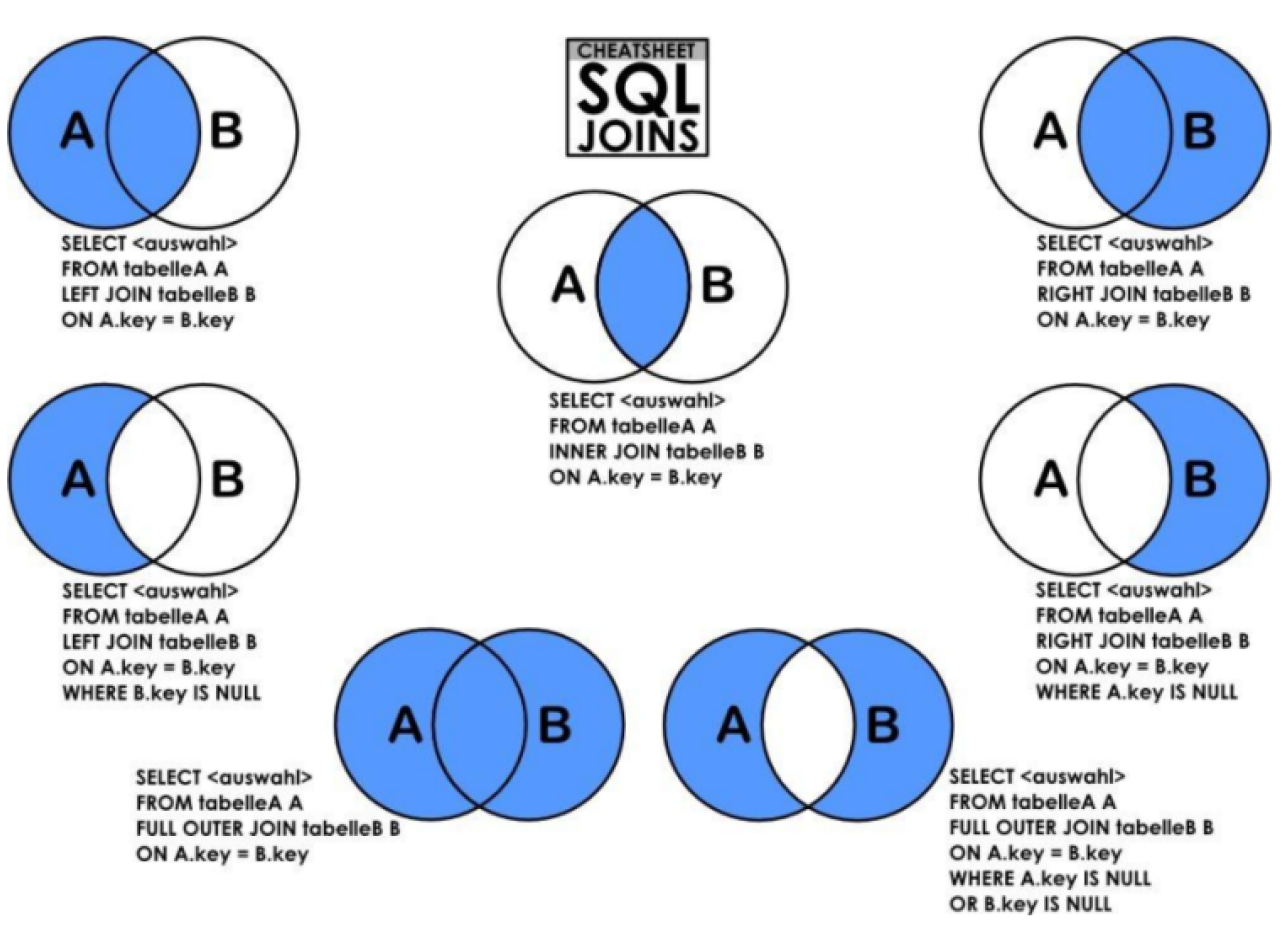
image.png
INNER JOIN
取两张表有对应关系的记录
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
select
cid
from
`course`
inner join `teacher` on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid;
LEFT JOIN
在内联的基础上保留左边表上没有对应关系的记录
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
select
course.cid
from
`course`
left join `teacher` on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid;
RIGHT JOIN
在内联的基础上保留右边表上没有对应关系的记录
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
select
course.cid
from
`course`
right join `teacher` on course.teacher_id = teacher.tid;
子查询/合并查询
单行子查询
- 01
select * from course where course.teacher_id = (select tid from teacher where tname = 'wood');
多行子查询
多行子查询返回多行记录的子查询
- IN 关键字:运算符可以检测结果集中是否存在特定的值,如果检测成功就执行外部的查询。
- EXISTS 关键字:内层查询语句不返回查询记录。而是返回一个真假值。如果内层查询语句查询到满足条件的记录,就返回一个真值(
true),否则,将返回一个假值(false)。当返回的值为true时,外层查询语句将进行查询;当返回的值为false时,外层查询语句不进行查询或查询不出任何记录。 - ALL 关键字:表示满足所有条件。使用 ALL 关键字时,只有满足内层查询语句返回的所有结果,才可以执行外层查询语句。
- ANY 关键字:允许创建一个表达式,对子查询的返回值列表,进行比较,只要满足内层子查询条件中的任意一个比较条件,就返回一个结果作为外层查询条件。
- 在 FROM 子句中使用子查询:子查询出现在
from子句中,这种情况下将子查询当做一个临时表使用。
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
select * from student where class_id in (select cid from course where teacher_id = 2)
select * from student where exists(select cid from course where cid = 5);
select student_id, sname from (select * from score where course_id = 1 or course_id = 2) as A left join student on A.student_id = student.sid;
正则
视图
视图(view)是一种虚拟存在的表,是一个逻辑表,本省没有数据,内容由查询定义。
基表:用来创建视图的表叫做基表
通过视图,我们可以查看基表的部分数据。视图数据来自定义视图的查询中使用的表,使用动态图动态生成。
优点
- 简单
- 安全
- 数据独立
语法
- 01
create view <视图名> as <select语句>
案例
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
create view view_learn as select (
A.student_id from (
select student_id, num from score where course_id = 1
) as A left join (
select student_id, num from score where course_id = 2
) as B on A.student_id = B.student_id
where A.num > if (isnull(B.num), 0, B.num)
);
流程控制
IF
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
if condition then
...
elseif condition then
...
else
...
end if
CASE
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
case value
when value then ...
when value then ...
else ...
end case
WHILE
- 01
- 02
- 03
while condition do
...
end while
LEAVE
- 01
- 02
-- 相当于break
leave label;
示例
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
-- leave语句退出循环或程序,只能和BEGIN ... END,LOOP,REPEAT,WHILE语句配合使用
-- 创建存储过程
delimiter //
create procedure example_leave(out sum int)
begin
declare i int default 1;
declare s int default 0;
while_label:while i <= 100 do
set s = s + i;
set i = i + 1;
if i = 50 then
leave while_label;
end if;
end while;
set sum = s;
end //
delimiter ;
call example_leave(@sum);
select @sum;
image.png
ITERATE
- 01
- 02
-- 相当于 continue
iterate label;
LOOP
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
-- 相当于 while(true){}
loop
...
end loop
-- 可以用LEAVE退出循环
示例
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
-- 创建存储过程
delimiter //
create procedure example_loop(out sum int)
begin
declare i int default 1;
declare s int default 0;
loop_label:loop
set s = s + i;
set i = i + 1;
if i > 100 then
leave loop_label;
end if;
end loop;
set sum = s;
end
//
delimiter ;
call example_loop(@sum);
select @sum;
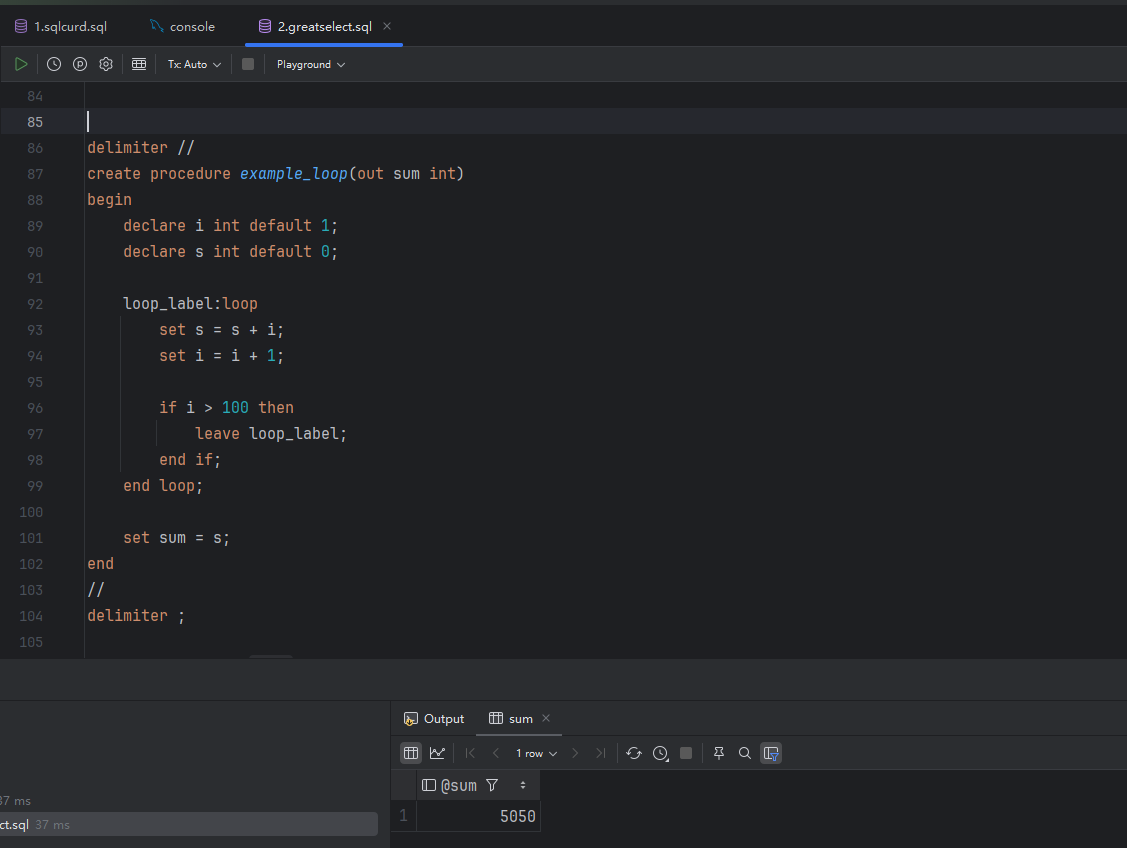
image.png
REPEAT
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
-- 相当于 do ... while(condition)
REPEAT
...
UNTIL condition
END REPEAT
示例
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
delimiter //
create procedure example_repeat(out sum int)
begin
declare s int default 1;
declare i int default 0;
repeat
set s = s + i;
set i = i + 1;
until i > 100
end repeat;
set sum = s;
end
//
delimiter ;
call example_repeat(@sum);
select @sum;
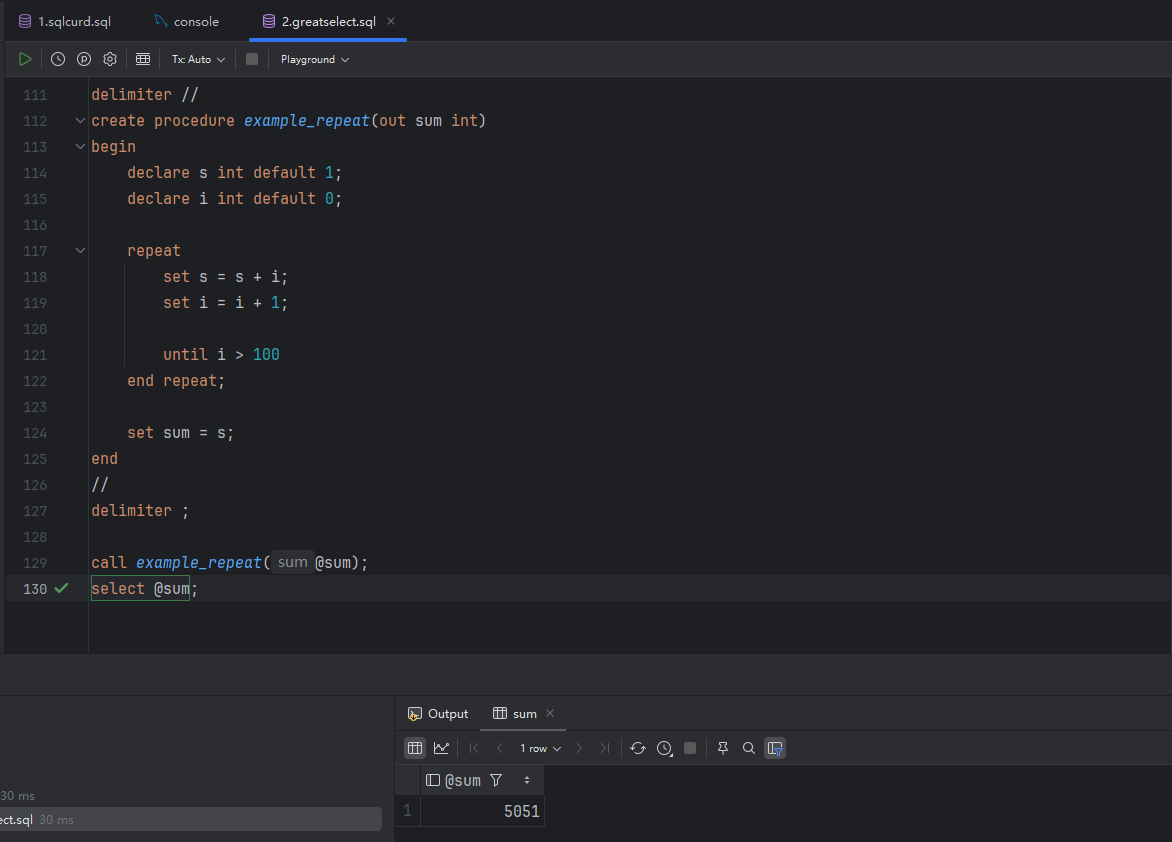
image.png
触发器
触发器(trigger)是 MySQL 提供给程序员和数据分析员来保证数据完整性的一种方法,他是与表时间相关的特殊存储过程,他的执行不是由程序调用,也不是手动启动,而是由事件来触发,比如当时对一个表进行 DML 操作(insert,delete,update)时就会激活他执行。
要素
- 监视对象:table
- 监视事件:insert,update,delete
- 触发时间:before,after
- 触发事件:insert,update,delete
语法
- 01
create trigger trigger_name trigger_time trigger_event on tbl_name for each row [trigger_order] trigger_body;
- trigger_bogy:可以使一个语句,也可以是多个语句;多个语句写在
BEGIN ... END之间; trigger_time: {BEFOER | AFTER};trigger_event: {INSERT | UPDATE | DELETE};trigger_order: {FOLLOWS | PRECEDES}
准备
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
create table `work` (
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`address` varchar(32)
)default charset = utf8 engine = innoDB;
create table `time` (
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`time` datetime
)default charset = utf8 engine = innoDB;
create trigger trig_test1 after insert on `work` for each row insert into `time` values (null, now());
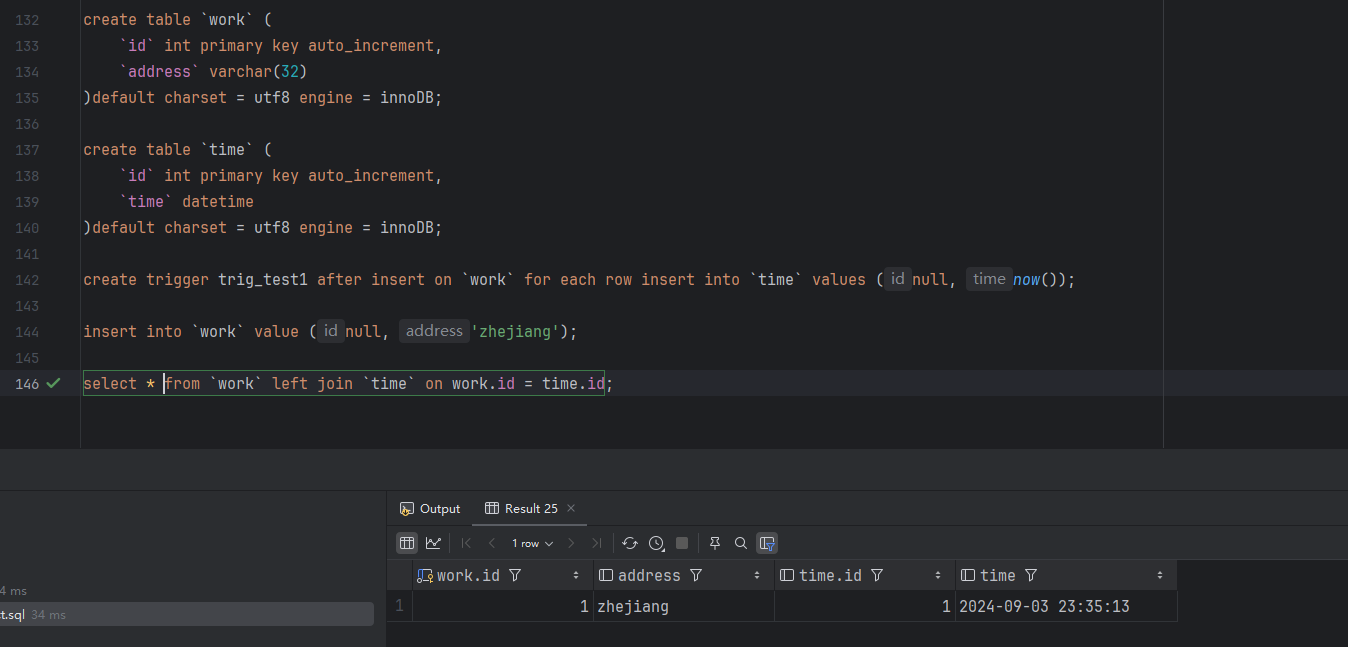
image.png
NEW 和 OLD
在 INSERT 类型触发器中,NEW 用来表示将要(BEFORE)或已经(AFTER)插入的新数据;
在 DELETE 类型触发器中,OLD 用来表示将要或已经被删除的源数据;
在 UPDATE 类型触发器中,OLD 用来表示将要或已经被修改的原数据,NEW 用来表示将要或已经修改为的新数据;
- 01
- 02
NEW.columnName
OLD.columnName
案例
在下订单的时候,对应的商品的库存量要相应减少,即买几个商品就减少多少个库存量。
准备
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
- 07
- 08
- 09
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
create table `goods` (
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(32),
`num` smallint default 0
);
create table `order` (
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`goods_id` int,
`quantity` smallint comment '下单数量'
);
insert into goods values (null, 'pig', 400);
insert into goods values (null, 'sheep', 500);
insert into goods values (null, 'bear', 600);
insert into `order` values (null, 1, 3);
insert into `order` values (null, 2, 4);
需求 1
客户修改订单数量,在原来购买数量的基础上减少 2 个;
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
delimiter //
create trigger trig_order_1 after insert on `order` for each row
begin
update goods set num = num - 2 where id = 1;
end//
delimiter ;
需求 2
客户修改订单数量,商品表的数量自动改变。
- 01
- 02
- 03
- 04
- 05
- 06
delimiter //
create trigger trig_order_2 before update on `order` for each row
begin
update goods set num = num + old.quantity - new.quantity where id = new.goods_id;
end //
delimiter ;
权限管理
创建用户
- 01
create user 'username'@'host' identified by 'password';
- host:指定该用户可以在哪个主机上登录,如果是本地用户可以用
localhost,如果想让该用户可以从任意远程主机登录,可以使用通配符%。
授权
- 01
grant privileges on databasename.tablename to 'username'@'host' with grant option;
- privileges:用户操作权限,如
select,insert,update等,如果要授予所有权限使用all; - with frant option:表是该用户可以将自己拥有的权限授予别人。
对使团授权
- 01
grant select, show view on `databasename`.`tablename` to 'username'@'host;
刷新权限
- 01
flush privileges;
远程连接
注释
mysqld.conf中的bind-address,修改mysql.user表,然后重启 mysql。
- 01
- 02
- 03
-- mysql.cnf
# vim /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysql.cnf
#bind-address=127.0.0.1
- 01
- 02
- 03
```sql
select `user`, `host` from `mysql`.`user`;
update user set host=% where user='root';

评论